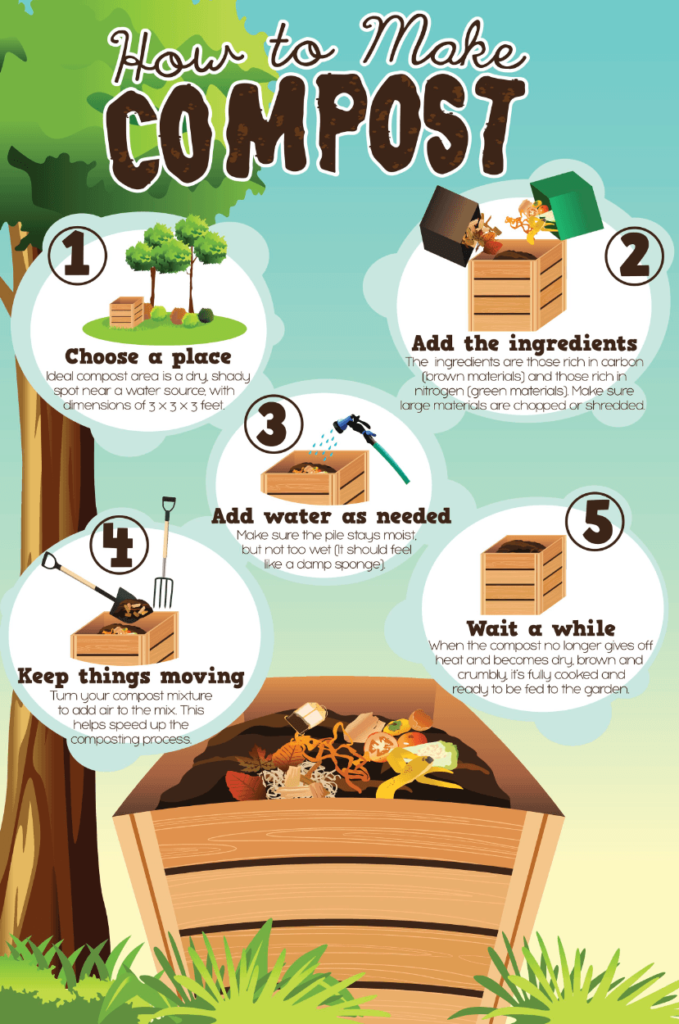
Composting at home is easier than you think. It turns kitchen scraps into rich soil.
Composting reduces waste and helps the environment. By composting, you recycle organic matter like food scraps and yard waste. This process turns them into valuable soil. Healthy soil helps plants grow better. Plus, it saves you money on fertilizers. Starting a compost pile at home is simple.
With the right tools and a bit of space, you can create nutrient-rich soil. This soil can be used in your garden or for houseplants. Composting is a small step that makes a big difference. Ready to start? Let’s dig into the basics of how to compost at home.
Table of Contents

Credit: greenecofriend.co.uk
Introduction To Composting
Composting is an easy and sustainable way to recycle organic waste. It involves breaking down food scraps and yard waste into nutrient-rich soil. This process can transform your kitchen leftovers into valuable compost for your garden. Let’s explore how to start composting at home.
Benefits Of Composting
Composting reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills. This helps decrease greenhouse gas emissions. It also enriches soil, helping plants grow healthier. By composting, you can save money on fertilizers. Additionally, composting can help reduce water usage in gardens. Healthy soil retains water better, needing less frequent watering.
Eco-friendly Living
Composting is an important part of eco-friendly living. It helps you reduce your carbon footprint. By recycling organic waste, you support a sustainable lifestyle. Composting also teaches valuable lessons about resource management. It helps you understand the natural cycle of growth and decay. This practice encourages you to make mindful choices about waste.

Credit: www.spokeandblossom.com
Choosing A Composting Method
Choosing a composting method is the first step in starting your composting journey. You can choose from various methods based on your space, time, and resources. Two popular methods are indoor and outdoor composting. Another effective technique is vermicomposting, which uses worms to break down organic matter.
Indoor Vs Outdoor
Indoor composting is suitable for those with limited outdoor space. You can compost in a small bin inside your kitchen or garage. This method allows you to manage waste without stepping outside. It’s also easier to control the composting environment indoors.
Outdoor composting requires a larger space, like a backyard. It can handle more waste and larger items. Outdoor bins or piles are common options. You need to turn the compost regularly to maintain airflow. Outdoor composting can attract pests if not managed well.
Vermicomposting
Vermicomposting uses worms to break down organic waste. Red wigglers are the most common worms for this method. They eat your kitchen scraps and produce nutrient-rich compost. You can do vermicomposting indoors or outdoors.
This method is efficient and fast. Worms can process waste quickly and produce high-quality compost. You need a special bin with bedding for the worms. Maintain the right moisture and temperature for the worms to thrive.
Setting Up Your Compost Bin
Composting at home can turn kitchen scraps and yard waste into rich soil. The first step is setting up your compost bin. This involves selecting the right bin and choosing an ideal location. Let’s dive into the details to get your compost bin ready for action.
Selecting A Bin
Choosing the right compost bin is crucial. You have several options. You can buy a ready-made bin or build one yourself. Ready-made bins come in various materials like plastic, wood, or metal. Each has its pros and cons. Plastic bins are lightweight and inexpensive. Wooden bins blend well with gardens. Metal bins last long but can rust.
If you prefer a DIY approach, wooden pallets or wire mesh can create an effective bin. Ensure the bin has good ventilation. Compost needs air to break down materials. A lid helps keep pests out and retains moisture. Size matters too. A small bin works for food scraps. Larger bins can handle yard waste.
Choosing A Location
The location of your compost bin affects its efficiency. Place the bin on bare soil. This allows worms and other beneficial organisms to enter. They help break down compost. Avoid placing the bin on concrete or asphalt. These surfaces block soil contact and slow down composting.
Select a shady spot. Compost needs warmth but direct sunlight can dry it out. A spot with some shade helps maintain moisture. Accessibility is also key. The bin should be easy to reach. You will add materials often, so a convenient location saves time.
Ensure there’s enough space around the bin. This allows for easy turning of the compost. Turning helps speed up the composting process. Keep the bin away from walls or fences to prevent moisture buildup.

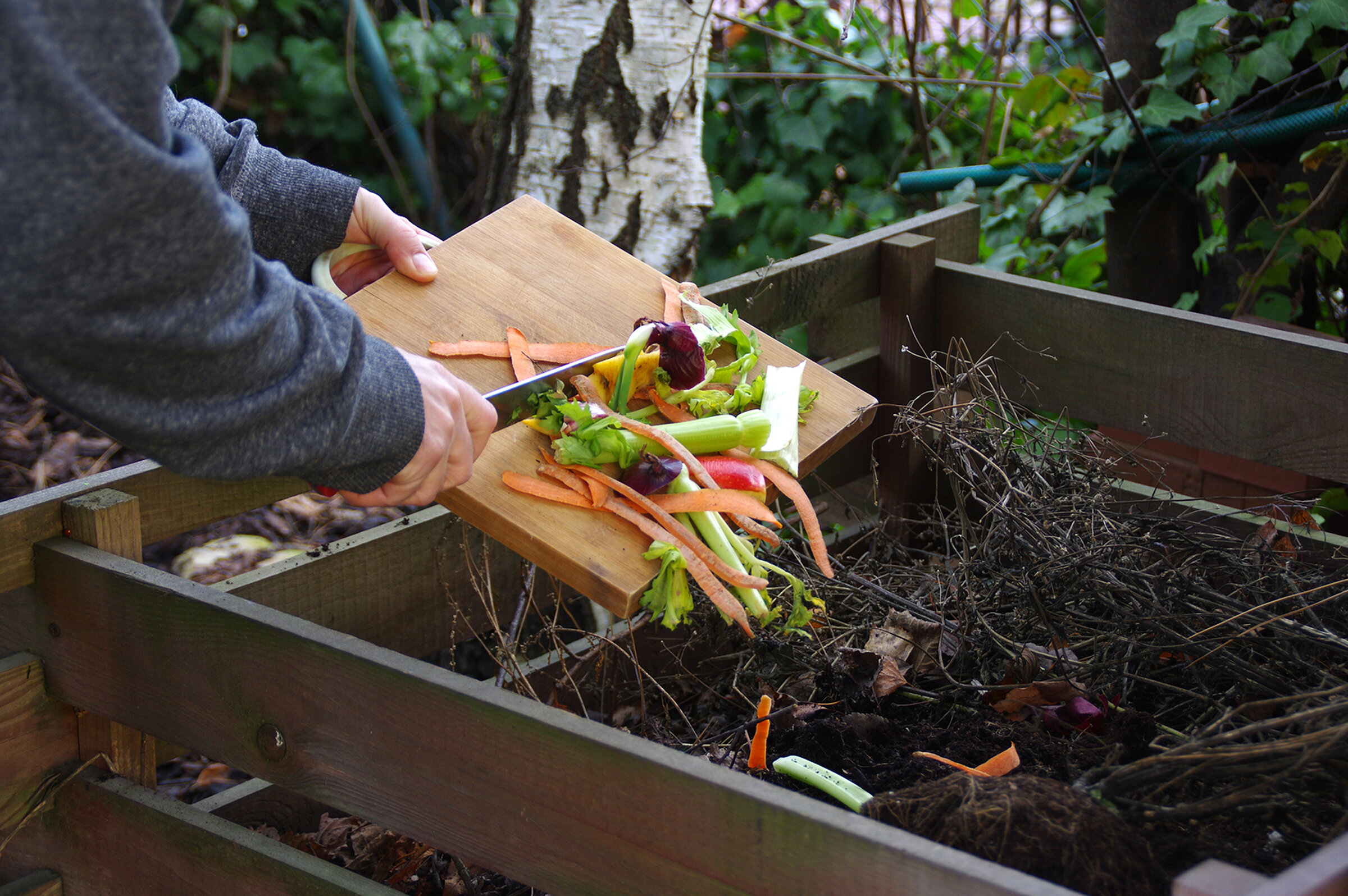
Materials For Composting
Creating compost at home is simple and eco-friendly. The right materials turn kitchen scraps into rich soil. We’ll look at the different types of materials needed. This will help you make the best compost for your garden.
Green Materials
Green materials are rich in nitrogen. They are moist and help with the composting process. Common green materials include:
- Vegetable scraps: These include peels, cores, and other leftovers.
- Fruit scraps: Use apple cores, banana peels, and citrus rinds.
- Coffee grounds: These are great for adding nitrogen.
- Grass clippings: Freshly cut grass is high in nitrogen.
- Manure: Use manure from herbivores like cows, horses, and rabbits.
Keep green materials in balance with brown materials. Too much green can make your compost pile smell bad.
Brown Materials
Brown materials are rich in carbon. They are dry and help balance the compost. Common brown materials include:
- Dry leaves: These are easy to find in the fall.
- Twigs and branches: Break them into smaller pieces.
- Cardboard: Tear it into small pieces before adding.
- Newspaper: Shred it and mix it well.
- Sawdust: Use untreated wood sawdust.
Brown materials help with airflow and structure. They prevent the compost from becoming too wet.
Balancing green and brown materials is key. It ensures fast and efficient composting. Aim for a ratio of 2 parts brown to 1 part green.
Maintaining Your Compost
Regularly turn your compost to ensure proper aeration and faster decomposition. Keep it moist but not too wet. Add a mix of green and brown materials for balance.
Maintaining your compost pile is key to turning kitchen scraps into rich soil. A well-maintained pile breaks down faster and smells better. It also keeps pests away. Here’s how to keep your compost in top shape.
Turning The Pile
Turning the pile helps aerate the compost. This means adding oxygen. Oxygen is vital for the microbes breaking down the materials. Use a garden fork or shovel to turn the pile. Aim to do this once a week. Turn the outer layers into the center. This helps mix the compost evenly.
Moisture Levels
Compost needs the right amount of moisture. Too dry and it won’t break down. Too wet and it can smell bad. Aim for a damp sponge feel. Add water if the pile is dry. Add dry materials if it’s too wet. Newspaper and dry leaves work well. Check moisture levels every week. Adjust as needed.
“`
Common Composting Problems
Composting at home can be rewarding, but sometimes issues arise. These problems can discourage even the most dedicated composters. Knowing how to tackle these common composting problems can make the process smoother. Let’s discuss some of the most frequent issues and how to solve them.
Odor Issues
One common problem is bad smells. A well-maintained compost pile should not stink. If your compost smells bad, it may be too wet or lack air. Turn the pile often to aerate it. Add dry materials like leaves or straw to balance moisture. Avoid adding meat, dairy, or oily foods. These can create unpleasant odors and attract pests.
Pest Control
Another common issue is pests. Rats, raccoons, and insects can invade your compost pile. To prevent this, avoid adding meat, bones, or fatty foods. Use a compost bin with a secure lid. Bury food scraps deep within the pile. This helps keep the pests away. If pests persist, consider using a pest-proof compost bin.
Harvesting Finished Compost
Harvesting finished compost is an exciting step in your composting journey. It means your hard work has paid off. Your organic waste has transformed into nutrient-rich soil. This compost can improve garden soil and promote plant health. Let’s explore how to know when your compost is ready and how to use it effectively.
Signs Of Readiness
How can you tell if your compost is ready? Here are a few clear signs:
- Color and Texture: Finished compost is dark brown or black. It looks like rich, crumbly soil.
- Smell: It smells earthy, like fresh soil. It should not smell like rotting food.
- Temperature: The pile is no longer warm. Active decomposition generates heat; finished compost is cool.
- Size: The pile has shrunk significantly. You’ll see a noticeable reduction in volume.
- Contents: Original materials are unrecognizable. No large chunks of food or yard waste should be visible.
How To Use Compost
Now that your compost is ready, here’s how you can use it:
- Soil Amendment: Mix compost into garden soil. This improves soil structure and adds nutrients.
- Mulch: Spread compost around plants. It helps retain moisture and suppress weeds.
- Potting Mix: Blend compost with other materials. Create a nutrient-rich mix for potted plants.
- Top Dressing: Apply a layer of compost on top of the soil. This enriches the soil with nutrients over time.
Remember, compost is a powerful natural fertilizer. It helps your plants grow strong and healthy. Happy composting!
Tips For Successful Composting
Composting at home is a great way to recycle kitchen scraps and yard waste. If done right, it turns waste into nutrient-rich soil. Here are some tips for successful composting to help you get started.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
To achieve optimal results, avoid these common composting mistakes:
- Too Much Green Waste: Adding too many kitchen scraps can make the pile wet and smelly. Balance with brown materials like leaves and paper.
- Neglecting Aeration: A compost pile needs air. Turn it regularly to avoid unpleasant odors and to speed up decomposition.
- Incorrect Moisture Levels: The pile should be as moist as a wrung-out sponge. Add water if it’s too dry, or dry materials if it’s too wet.
Seasonal Composting Tips
Composting needs change with the seasons. Adjust your practices accordingly:
| Season | Tips |
|---|---|
| Spring | Add fresh green materials from garden clean-up and kitchen scraps. |
| Summer | Keep the pile moist. Add water if needed and avoid excessive heat. |
| Fall | Incorporate fallen leaves and garden waste. Chop large pieces to speed up decomposition. |
| Winter | Insulate the pile with straw or cover it to keep warmth in. Composting slows but doesn’t stop. |
By following these tips, your composting efforts will be more successful and rewarding. Happy composting!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Composting At Home?
Composting at home is the process of recycling organic waste. It involves converting kitchen scraps and yard waste into valuable compost. This compost can enrich soil and help plants grow.
What Materials Can Be Composted?
You can compost vegetable scraps, fruit peels, coffee grounds, and yard clippings. Avoid meat, dairy, and oily foods. These can attract pests and cause odors.
How Do I Start A Compost Pile?
Start a compost pile by layering green and brown materials. Add kitchen scraps and yard waste. Keep the pile moist and turn it regularly to aerate.
How Long Does Composting Take?
Composting typically takes between two to six months. The process can be sped up by turning the pile frequently. Proper moisture and aeration are key.
Conclusion
Composting at home is simple and rewarding. It helps reduce waste. You can create rich soil for your garden. Start small and learn as you go. Use kitchen scraps and yard waste. Turn the compost regularly for best results. Patience is key; good compost takes time.
Enjoy the benefits of a healthier garden and a greener planet. Happy composting!